Acronyms The Acronyms found in the selected table (typically the Acronyms table) is rendered into a tabular list of Acronyms. Title and text strings found in the Misc Text table are rendered as the section title and preamble using the style settings found for each. Requires a valid table be selected.
Begin Document Setup Establishes basic style settings with the target document. Sets header, footer, watermark, and other details. Tags insertion point for later TOC entries.
Data Elements The data concepts found in the selected table (typically the Data Elements table) are rendered into a numbered section of data concepts. The initial title and text strings found in the Misc Text table for this step are rendered as the section title and preamble using the style settings found for each. Each data concept is given its own title based on its name and the type of record that it is (message, data frame, data element etc.). Each entry is rendered according to the current options settings. If the data concept is NOT in the same FADD as the current default FADD, then its mapping is listed. If the options have selected a used in list of associated data concepts, the tables enabled in the Dialog will be used to determine relationships. Typically three bookmarks are made for each entry as well (the entry itself, the ASN, and the XML). A wide variety of rendering styles can be selected; see the Options Area for further details. Requires a valid table to be selected.
Data Frames The data concepts found in the selected table (typically the Data Frames table) are rendered into a numbered section of data concepts. The initial title and text strings found in the Misc Text table for this step are rendered as the section title and preamble using the style settings found for each. Each data concept is given its own title based on its name and the type of record that it is (message, data frame, data element etc.) Each entry is rendered according to the current options settings. If the data concept is NOT in the same FADD as the current default FADD, then its mapping is listed. If the options have selected a used in list of associated data concepts, the tables enabled in the Links... Dialog will be used to determine relationships. Typically three bookmarks are made for each entry as well (the entry itself, the ASN, and the XML). A wide variety of rendering styles can be selected; see the Options Area for further details. Requires a valid table to be selected.
Deprecated Entries The data concepts found in the selected table (typically the Deprecated table) are rendered into a numbered section of data concepts. The initial title and text strings found in the Misc Text table for this step are rendered as the section title and preamble using the style settings found for each. Each data concept is given its own title based on its name and the type of record that it is (message, data frame, data element etc.) Each entry is rendered according to the current options settings. If the data concept is NOT in the same FADD as the current default FADD, then its mapping is listed. If the options have selected a used in list of associated data concepts, the tables enabled in the Links... Dialog will be used to determine relationships. Typically three bookmarks are made for each entry as well (the entry itself, the ASN, and the XML). A wide variety of rendering styles can be selected; see the Options Area for further details. Requires a valid table to be selected.
Dialogs The data concepts found in the selected table (typically the Dialog s table) are rendered into a numbered section of data concepts. The initial title and text strings found in the Misc Text table for this step are rendered as the section title and preamble using the style settings found for each. Each data concept is given its own title based on its name and the type of record that it is (message, data frame, data element etc.) Each entry is rendered according to the current options settings. If the data concept is NOT in the same FADD as the current default FADD, then its mapping is listed. If the options have selected a used in list of associated data concepts, the tables enabled in the Links... Dialog will be used to determine relationships. Note that one does not expect to see Dialog s link to other entries in this way, so this should be empty. A wide variety of rendering styles can be selected; see the Options Area for further details. Requires a valid table to be selected.
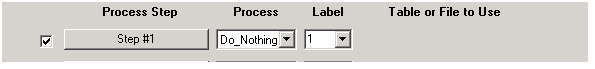
Do Nothing A void step. No changes in the document occur.
External Entries The data concepts found in the selected table (typically the EternalDEs table) are rendered into a numbered section of data concepts. The initial title and text strings found in the Misc Text table for this step are rendered as the section title and preamble using the style settings found for each. Each data concept is given its own title based on its name and the type of record that it is (message, data frame, data element etc.) Each entry is rendered according to the current options settings. If the data concept is NOT in the same FADD as the current default FADD, then its mapping is listed. Note that with External Entries this is typically the case. If the options have selected a used in list of associated data concepts, the tables enabled in the Links... Dialog will be used to determine relationships. Typically three bookmarks are made for each entry as well (the entry itself, the ASN, and the XML). A wide variety of rendering styles can be selected; see the Options Area for further details. Requires a valid table to be selected.
Include File The selected file is included in the current document at the current selection point. The styles of the included document are NOT used (the style of the master document being built takes precedence). Commonly used for adding content that is not created from the database tables. Requires a valid file and path to be selected.
ITIS Phrases A processing step used to render the sub-categories used in ITIS codes. The various natural language sentences found in this standard are actually created here in this step as well as adjusting what code values are not reserved for national use with each edition.
Link All Files Used in multiple-document rendering runs. This step uses the dynamic list of bookmarks and linkages which was built up over multiple documents and performs the hyper linking resolution using that list. Thus, each document is cross linked to others in its family in one step. Note that, unlike the Multi-linker tool, this step does not require the re-naming of the files with temporary names until the last linking step is performed.
Messages The data concepts found in the selected table (typically the Messages table) are rendered into a numbered section of data concepts. The initial title and text strings found in the Misc Text table for this step are rendered as the section title and preamble using the style settings found for each. Each data concept is given its own title based on its name and the type of record that it is (message, data frame, data element etc.) Each entry is rendered according to the current options settings. If the data concept is NOT in the same FADD as the current default FADD, then its mapping is listed. If the options have selected a used in list of associated data concepts, the tables enabled in the Links... Dialog will be used to determine relationships. Typically three bookmarks are made for each entry as well (the entry itself, the ASN, and the XML). A wide variety of rendering styles can be selected; see the Options Area for further details. Requires a valid table to be selected.
Next File Used in multiple-document rendering runs. This step closes the current document, and opens the next document (using the same template files). The dynamic list of linkages (bookmarks) continues to be built, hence spanning over multiple documents when completed.
Pause A way to stop the script to allow manual intervention of some type. A modal Dialog is displayed asking the user to continue. This Dialog may also prompt the user regarding what they are supposed to be doing during this pause.
Start Word Default first step. Used to establish the automation between the application and the MS Word instance. Confirms existence of the needed basic styles in the template document. Deletes the old copy of the target file, if it exists.
Terms The terms found in the selected table (typically the Terms table) are rendered into a numbered list of terms. Title and text strings found in the Misc Text table are rendered as the section title and preamble using the style settings found for each. Requires a valid table be selected.
TOC Finish The TOC and Finish step adds some final time stamps, appends a table of contents (TOC) at the insertion point determined during the initial phases, and then builds up all the hyperlinks for the document (if selected). The process of building the hyperlinks is typically the longest phase of the entire process, exceeding all the other phases combined. The basic algorithm being applied here is to seek for any possible place an existing bookmark could connect to and to place a hyperlink there. This involves an exhaustive search over the document for matching strings found in conjunction with the right style and in the proper code context. When completed, the TOC is updated to reflect page changes and the document rendering is then finally completed.
 |
A few remarks about the technical details of the hyperlinking process in document creation, which is somewhat counter intuitive in nature. When an entry is created from a data concept, a hyper link "bookmark" is also created for it (in fact there are typically three of them, the top of the entry itself, the ASN and the XML each have a link entry). There are some problems to overcame with name collisions here, which can result in a number being appended to the actual bookmark used. This is all that occurs when the entry is added to the word document (the links are calculated and the the used-in linking text is added at this time as well as well formed text but no links are yet preset). The next entry is processed until the end of that table or section is reached. Note that in fact the 1st Word tool can not actually link to the other sections at this point because those other sections may not have been written out to the document yet. The actual linking is done in the clean up part of the process, typically the last step of the run. At this point each and every bookmark that was created is used to seek over the entire document for places that hyper-links could be placed. This is the visible jumping about you see at the end of the document run. The initial matching process uses a combination of the string itself and the Word text/paragraph style that the string appears in. This allows the document author to sew together not only the ASN/XML of the standard also but any document sections with code fragments or examples that he wants to (simply by controlling the style sheet that was used). When a "match" is found the tool uses the same parser logic found in Mini-Edit to extract the surrounding text and determine if the local context is a valid instance of the name (not a sub string and not inside some kind of code comment, and matching any proper name space, etc). If all this checks out, a hyper-link is placed into the document. Note that this produces links both "up" to other data concepts that use the entry and "down" to other data concepts used by and found within the listing. Note that besides the ASN/XML and records, the tool can link to terms and acronyms in this way as well; see the Options page. You can also use a Multi-linker tool to link to the standard from other external documents, the long term intent of this is to allow linking back to the relevant pages of a standard from other documents. So, in summary, the process of link creating is a bit bass-ackwards from what people might expect. |